FOOD THAT SUPPORTS MENTAL HEALTH

In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the connection between nutrition and mental health. Just as certain foods can help the body grow strong, some foods specifically support mental well-being. For families and caregivers, understanding these nutritional choices can empower them to make decisions that promote better mental health outcomes for their loved ones.
Key Nutrients for Mental Health
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Essential for brain health, omega-3 fatty acids can be found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. These nutrients are linked to lower levels of depression and anxiety, making them a critical component of a mental health-friendly diet.
2. Antioxidants: Antioxidant-rich foods combat oxidative stress in the brain, which can exacerbate mental health disorders. Berries, such as blueberries and strawberries, and dark chocolate provide a delicious source of these beneficial compounds.

3. Vitamins and Minerals: Essential vitamins and minerals support brain function and mood regulation. Leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are excellent sources of B-vitamins, magnesium, and zinc, which can boost overall mental well-being.

4. Probiotics:The gut-brain connection is increasingly recognized in mental health care. Probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi promote a healthy gut microbiome, which is integral to mental wellness.

5. Hydration: Adequate hydration is vital for maintaining cognitive function and mood stability, so regular water intake should not be overlooked.

Integrating Nutritional Support in Mental Health Care
For individuals living with mental health disorders, nutritional support should be an integral part of their care plan. Healthcare services staff can be trained to work collaboratively with nutritionists and other healthcare professionals to develop tailored dietary plans that bolster mental health.
1. Collaborative Care: Teams comprised of dietitians, mental health professionals, and primary care providers can create comprehensive care plans. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that nutritional interventions are appropriately integrated into the overall treatment plan.

2. Education and Training: Staff in both home care and group home settings should receive training on the importance of nutrition in mental health. Understanding how to prepare and offer meals that support mental well-being empowers caregivers to make impactful contributions to their clients' health.
3. Personalized Nutrition Plans: Just as each individual’s mental health needs are unique, so too are their nutritional requirements. Collaborative teams can develop personalized nutrition plans, considering dietary preferences, medical conditions, and cultural influences.
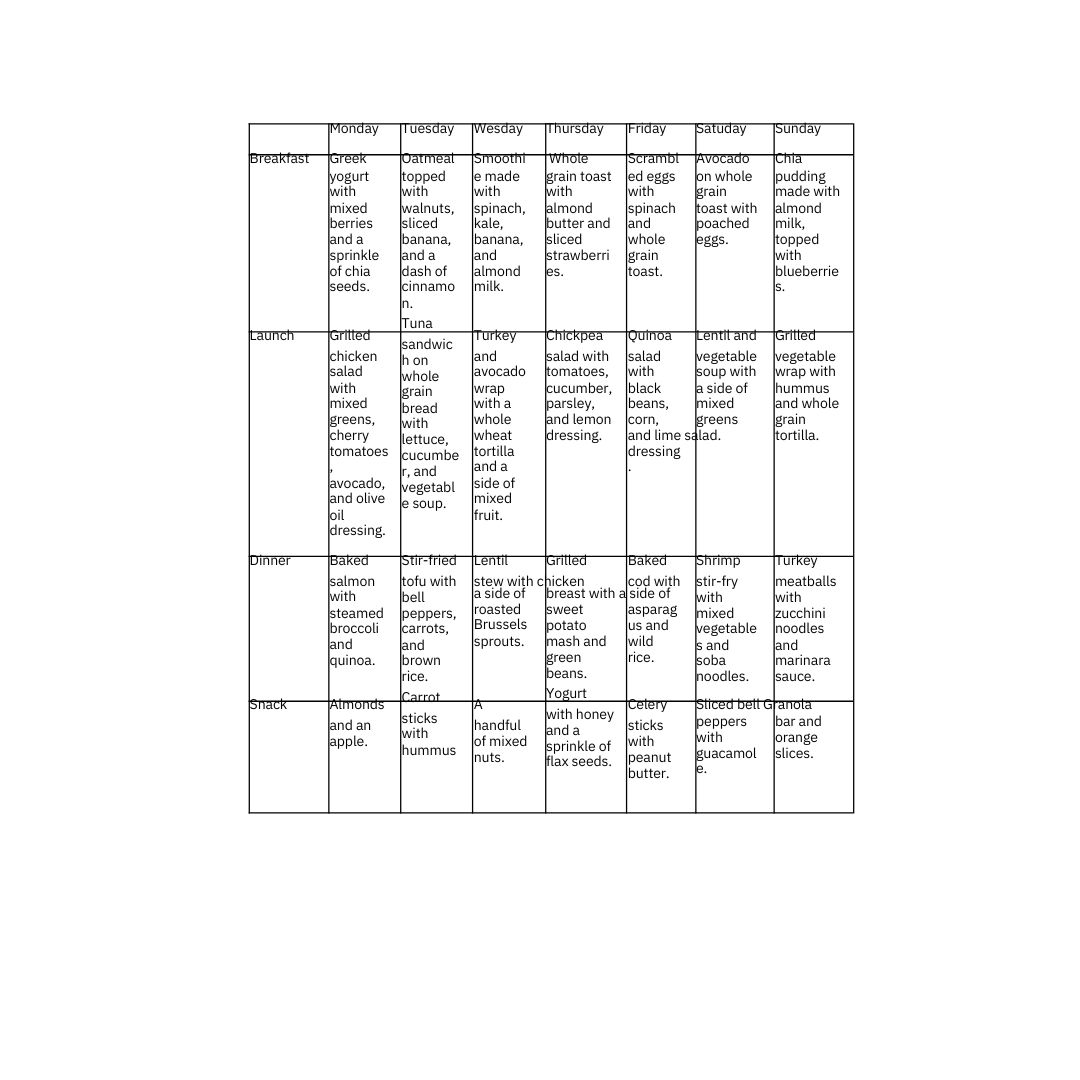
4. Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment: Nutritional plans should be dynamic, with regular assessments to adjust based on the individual's progress and any changes in their mental health status.
By prioritizing nutritional support and fostering collaboration among healthcare professionals, families and caregivers can enhance the mental well-being of those in their care. Thoughtful food choices, along with professional collaboration, can contribute significantly to the holistic approach needed for effective mental health care, empowering individuals to thrive in both home and group settings.